What is an Air Compressor? A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of machinery and industrial applications, air compressors play a crucial role, providing a versatile source of power for various tools and processes. This powerful device serves as the heart of various tools and systems, providing compressed air for a wide range of tasks. In this article, we’ll delve into the fundamentals of air compressors, exploring their functions, types, and the diverse applications that make them indispensable.
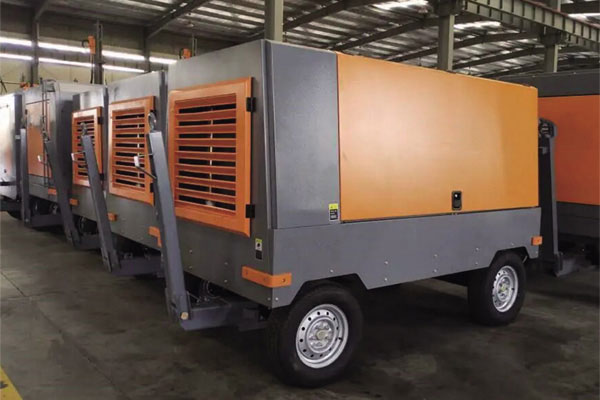

What is an Air Compressor?
An air compressor is a mechanical device designed to convert power into potential energy stored in compressed air. It works by drawing in atmospheric air and compressing it to a higher pressure using a motor or an engine. The compressed air is then stored in a tank, ready for use in various applications.
How Does an Air Compressor Work?
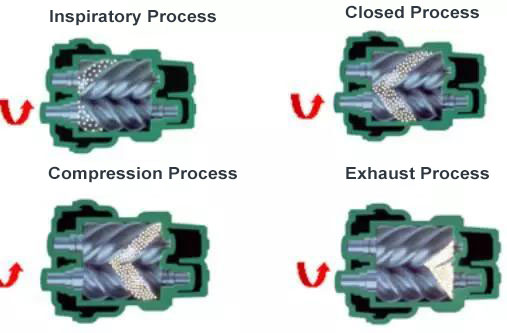
The working principle of an air compressor is relatively straightforward. It involves the following key components:
1. Motor or Engine:
The source of power, whether it’s an electric motor or a gasoline engine, drives the compressor.
2. Air Intake:
Air is drawn into the compressor through an intake valve.
3. Compression Chamber:
Once inside, the air is compressed within a chamber. Compressors can be categorized into two main types based on their compression mechanism: positive displacement compressors and dynamic compressors.
- Positive Displacement Compressors: These compressors work by trapping a fixed amount of air and then reducing its volume. Common types include reciprocating (piston) compressors and rotary screw compressors.
- Dynamic Compressors: These compressors accelerate the air to high velocity and then decelerate it to increase its pressure. Centrifugal compressors fall into this category.
4. Pressure Regulator:
The pressurized air is then regulated to the desired pressure level using a pressure regulator.
5. Storage Tank:
In many setups, the compressed air is stored in a tank, creating a reserve that can be used as needed.
Types of Air Compressors:
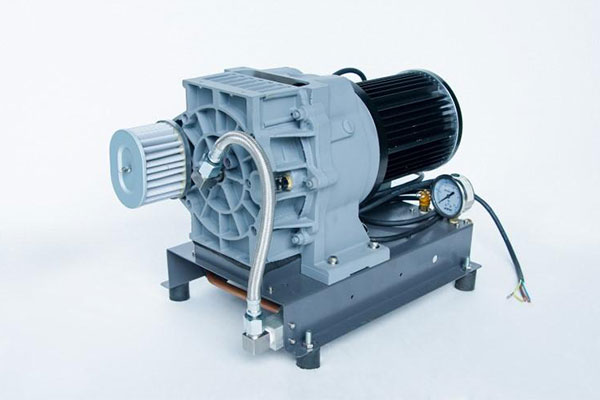
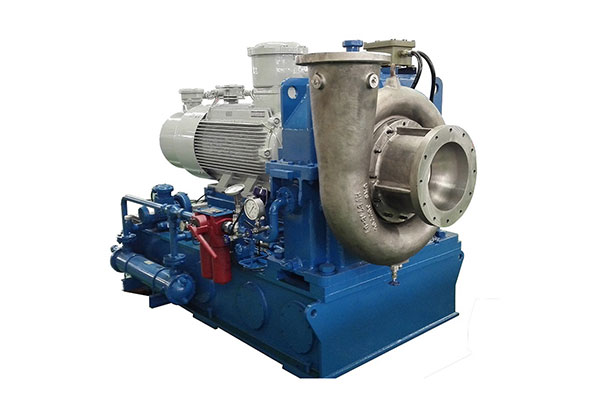




Air compressors come in various types, each designed for specific applications. The two primary categories are positive displacement compressors and dynamic compressors.
Positive Displacement Compressors:
- Reciprocating Compressors: Utilizing pistons to compress air, reciprocating compressors are commonly found in smaller applications and industries.
- Rotary Screw Compressors: These compressors use a pair of interlocking screws to compress air, offering a continuous and steady flow.
- Scroll Compressors: Known for their quiet operation, scroll compressors use spiraled scrolls to compress air efficiently.
Dynamic Compressors:
- Centrifugal Compressors: Employing a high-speed impeller, centrifugal compressors are ideal for large-scale industrial applications, providing high volumes of compressed air.
Applications of Air Compressors:

Air compressors find applications across a wide range of industries, contributing to efficiency and productivity. Some common uses include:
- Powering Pneumatic Tools: Air compressors are often used to operate pneumatic tools such as nail guns, impact wrenches, and spray guns.
- Industrial Processes: Many manufacturing processes rely on compressed air for tasks like cutting, molding, and packaging.
- HVAC Systems: Air compressors play a crucial role in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, helping to regulate air flow and pressure.
- Painting and Surface Finishing: Spray painting and surface finishing applications benefit from the controlled and consistent airflow provided by air compressors.
Choosing the Right Air Compressor:

Selecting the appropriate air compressor depends on factors such as the intended application, required pressure, and volume of compressed air. Considerations include:
- Horsepower and Capacity: Matching the compressor’s power to the demand of your tools or processes.
- Duty Cycle: Understanding the duty cycle to ensure the compressor can handle continuous operation if necessary.
- Tank Size: Choosing a suitable tank size for applications that require a steady supply of compressed air.
Conclusion:
Understanding what an air compressor is and how it functions is crucial for appreciating its significance in diverse industries. Whether it’s powering tools, supporting manufacturing processes, or contributing to medical advancements, the air compressor plays a pivotal role in making our daily lives more efficient and convenient.

